DC motor is ? The following is the definition, type, parts and also the working principle of DC Motor equipped with examples
Do you already know what a DC Motor is? Some of us who are often involved in the world of automotive and electronics must be familiar with the term DC motors.
These devices are generally applied to electronic devices, including household appliances, industrial machines, DC fans, DC electric drills, and others. Here’s a more complete review.
Definition of DC Motor
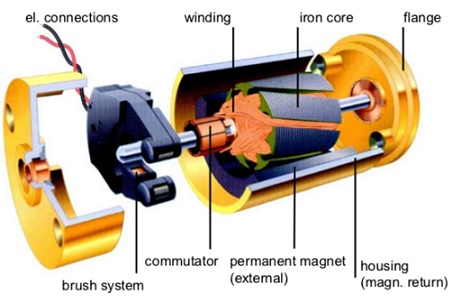
The definition of a DC motor is an electronic device that can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The way a DC motor works in converting energy is by taking electrical power through direct current which is then converted into mechanical rotation.
DC motors are also known as electric motors or direct current motors. DC motor can also be interpreted as a device that can convert electrical energy into motion or kinetic energy. The following is an example of the application / use of DC motors in modern technology:
- Application of DC motor as a sliding door drive in the automation of database storage room monitoring system using PLC omron CPM1A I/O 30
- The application of the Thyristor rectifier full-wave one-stroke on the directional control of the rotation of the DC motor to reverse the direction of rotation and rotation to the left.
- DC motor applications use parallel ports in a simple robotic circuit that is controlled using a computer and parallel ports.
Also Read: Definition and Function inductor and its types
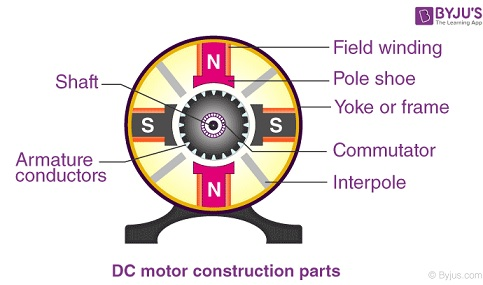
DC Motor Parts
Street : byjus.com
Dc motor components consist of a stator, armature, rotor and commutator with a brush. The opposite polarity between the two magnetic fields inside the DC motor that causes the rotation.
To make it easier to understand the components and functions, here we explain the DC motor parts complete with pictures and functions:
-
Rotor (Armature)
The rotor is one of the parts of a DC motor which is also often called an armature. The component rotates and is between the poles of the fields windings. Some of the particles that make up the rotor include the core, commutator, shaft, and rotor windings.
The rotors on the DC motor are magnetic laminated cylinders isolated from each other. The position of this rotor is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder. It is this rotor that will rotate rotating on its axis and separated from the field coil by an air gap.
-
Stator (Coil Field)
The stator is one part of the motor, but it does not move, but is stationary. The constituent particles consist of several components, including the core, winding, and stator frame.
On the frame part it is made using cast iron, as well as being home to the entire element of the generator. This one component is a DC motor part in the form of a wire winding that will produce a magnetic field. This part is a static/ immovable part.
-
Engine Body
The components of the machine body have a function as a medium for the flow of magnetic flux produced by the two magnetic poles. In addition, the machine body also has the function of laying certain tools that surround part of the machine. Generally, the body of this machine is made of steel plate material or cast iron.
-
Commutator (Komutator)
A commutator is a cylindrical structure made of copper stacked but insulated to each other using mica. The main function of the commutator is to supply electric current to the winding of the coil.
-
Brush ( Sikat Motor DC)
The carbon brush is located on the commutator and is useful for providing an electrical voltage supply to the motor. The motor mechanically can cause certain problems in an environment.
It takes some maintenance when wearing the motor. The action of the carbon brush or the presence of movement on the commutator can cause a spark.
These brush components are made of graphite and carbon structure. The brush on the DC motor plays a role in conducting electric current from the outer circuit to the rotating commutator.
-
Belitan Armor
This component is often also known as Armature winding, which is part of a DC motor whose role is to generate a static magnetic field in the rotor.
Therefore, we understand that commutators and brush units relate to the transmission of power from a static electrical circuit to a mechanically rotating region or rotor.
-
Frame (Yoke)
This dc motor part is a protector (protector) of the stator and rotor. The frame or yoke protects all the components in it.
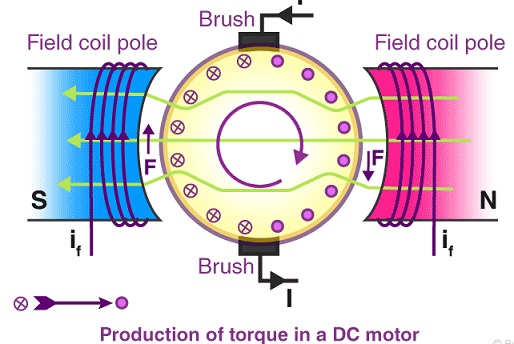
Working Principle of DC Motor
Street : byjus.com
Basically, the working principle of the DC motor is to reverse the negative phasa of a sinusoidal wave into a wave that has a positive value using a commutator.
Thus the current that reverses direction with the anchor coil rotating in a magnetic field, generated voltage (GGL). Here is the mechanism of the working principle of DC motors in general:
- The electric current in the magnetic field will give a force
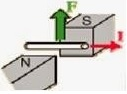
- If the current-carrying wire is formed like a circle (Loop), then both sides of the loop i.e. at the right angle of the magnetic field will gain force in the opposite direction.
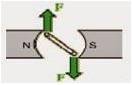
- The two forces generated will form a rotating force (torque) which later plays a role in rotating the coil.
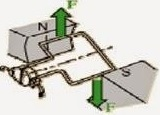
- The loop on the dynamo will provide uniform rotational power.
- The magnetic field is obtained from an electromagnetic array called a field coil.
In conclusion, the working principle of a DC motor is that if current passes on a conductor, a magnetic field arises around the conductor. The magnetic field only occurs around a conductor if there is current flowing in the conductor. The direction of the magnetic field is determined by the direction of flow of current on the conductor
Overview of How DC Motors Work:
DC motors have two main components, namely the rotor and stator. To be able to move, the working principle of a DC motor uses the phenomenon of an electromagnet.
When the electricity reaches the coil, the north surface will automatically move towards the south side magnet.
Then, the coil on the south side magnet moves towards the north side of the magnet.
In this case, a meeting occurs between the two sides of the magnet, then it causes the presence of mutually attractive reactions, thereby impacting the cessation of movement in the coils.
In order to move again, the magnetic poles and the coil must face each other, so that the direction of electricity in the coil is reversed.
In this situation, the north pole on the coil will switch to the south, and vice versa. When this happens, then the south pole becomes opposite to the south pole.
Such is the case with the north pole. This will cause a mutually rejecting reaction. So that it will automatically cause the movement of the coils.
The coil rotates until its north pole is again facing the south pole side.
The cycle of how the dc motor works occurs repeatedly until the disconnection of the coil with electricity. So, when there is no electricity, the cycle will stop by itself.
Also Read: Definition and Function fuses and how to measure it
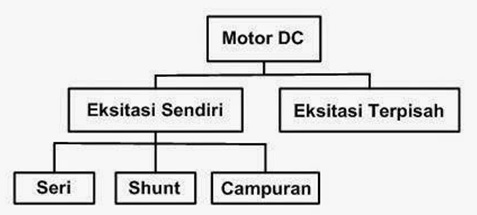
DC Motor Type
-
Self Excited DC Motor
A dc electric motor gets a current flow source which is a magnetic amplifier in the absence of a special source, but rather from the device itself.
If based on the relationship of the winding on the magnetic amplifier with the one in the anchor, then this motor can be grouped into several types, including series motors, compound motors, and shunt motors. You can see the details below:
-
DC Motor Series
DC motors are the best type, because they can move both at low and high electrical power. Tools that use this type of motor are vacuum cleaners, hair dryers, elevators, and others.
-
Motor DC Shunt
This type of motor is used in tools that require speed stability. Some of the tools that apply this motor include fans, drill tools, wipers, blowers, and others.
-
Motor DC Brushless
This type of motorbike is without wearing a brush and has advantages in terms of speed, efficiency, and control. The equipment that applies this type of motor is a heating device, a small cooling fan, a printer, and so on.
-
Motor DC Exitasi Terpisah (Separately Excited DC Motor)
This type of device obtains a source of electricity from a certain source, which is separate from the current source to the rotor. In this case, the flow of electricity to the anchor is not bound by the magnetic amplifier current.
DC Motor Speed Regulation
-
Anchor Voltage Control
If the voltage on the anchor of the motor is a series with a separate gain that is taking place with a decrease in speed, the torque will also drop as a result. So that the motor torque becomes smaller than the load torque. This causes the motor speed to decrease until the amount of motor torque is equal to the load torque.
-
Terrain Control
The speed regulation of the dc motor can be done by controlling the terrain. This is done with the system if the flux on the terrain is lowered, resulting in an increase in motor speed. But it is very unfortunate, this method can cause some problems in terms of efficiency, so it is quite rarely used.
The existence of a DC motor makes electronic devices can be used as their functions. Thus, it can be understood that the device plays a fairly important role in the power tools that you usually use every day. Then it must be ensured that this component can function as it should.



