Definition and Function of Potentiometer, – In Electronic Equipment, potentiometer are often found that function as Volume regulators in Audio / Video equipment such as Radio, Walkie Talkie, Car Tape, DVD Player and Amplifier. Potentiometers are also often used in light dimmer circuit and voltage regulatory in power supply (DC generator). So what exactly is a potentiometer?
Potentiometer (POT) is one type of Resistor whose Resistance Value can be adjusted according to the needs of the Electronic Circuit or the needs of the wearer. Potentiometer are a family of resistors that belong to the Variable Resistor Category. Structurally, the potentiometer consists of a 3-foot terminal with a shaft or lever that serves as its regulator. The figure below shows the Internal Structure of the Potentiometer and its shapes and symbols.

Potentiometer Structure and Its Shapes and Symbols
Basically the important parts in the Potentiometer Component are:
- Sweeper or also called Wiper
- Resistive Element
- Terminal
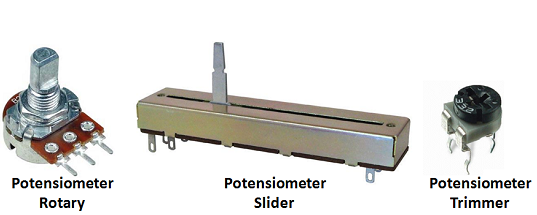
Types of Potentiometer
Based on its shape, potentiometer can be divided into 3 types, namely:
-
Slider Potentiometer
which is a Potentiometer whose resistance value can be adjusted by sliding its Wiper from left to right or from bottom to top according to its installation. Usually use the Thumb to shift the wipers.
-
Rotary potentiometer
which is a potentiometer whose resistance value can be adjusted by rotating its wiper along a circular trajectory. Usually use the Thumb to rotate the wipers. Therefore, Rotary Potentiometer is often called thumbwheel potentiometer.
-
Trimmer
potentiometer, which is a potentialometer that is small in shape and must use a special tool such as a screwdriver (screwdriver) to rotate it. Trimmer potentiometers are usually paired in PCBs and are rarely adjusted.
Working Principles (How to Work) Potentiometer
A potentiometer (POT) consists of a resistive element that forms a path (track) with terminals at both ends. While the other terminal (usually in the middle) is a Sweeper (Wiper) which is used to determine movement on the path of the resistive element (Resistive). The Movement of the Sweeper (Wiper) on the Resistive Element Path is what regulates the rise and fall of the Resistance Value of a Potentiometer.
Resistive Elements in Potentiometers are generally made of a mixture of Metal (metal) and Ceramic or Carbon (Carbon) Materials.
Based on the track (path) of resistive elements, potentiometers can be classified into 2 types, namely Linear Potentiometers (Linear Potentiometers) and Logarithmic Potentimic Potentiometers.
Potentiometer Functions
With the ability to change resistance or resistance, potentiometers are often used in electronic circuits or equipment with the following functions:
- As a Volume regulator on various Audio / Video equipment such as Amplifiers, Car Tapes, DVD Players.
- As a Voltage Regulator on the Power Supply Circuit
- As a Voltage Divider
- TRIAC Switch App
- Used as Joystick on Tranducer
- As a Signal Level Controller
Also read: How to Measure Potentiometer with Multimeter



