Have you found out about thermal overload relay devices? What is the role of the device? And what are the components in it? Let’s review it in detail here.
The use of thermal overload relays (TOR) will effectively increase the life of your electric motor and reduce the risk of costly damage.
In this article, you will gain a deeper understanding of this component and how to use it. Let’s start by understanding the meaning of thermal overload relay (TOR).
Definition of Thermal Overload Relay

Sample image of Thermal Overload Relay Image
Thermal overload relay (TOR) is a component used to protect electric motors from overheating or overload. TOR is responsible for detecting excessive temperatures in electric motors and taking measures to prevent further damage.
TOR serves to protect the electric motor from overheating or overload. When TOR detects excessive temperature in the electric motor, this component will cut off the electrical power flowing to the motor. In this way, the thermal overload relay can prevent the electric motor from further damage.
TOR must also be appropriately regulated in order to operate effectively. In manual mode, TOR can be manually set to disconnect the electrical power on the electric motor if excessive temperature is detected. While in automatic mode, TOR will operate automatically according to the temperature of the electric motor.
By using thermal overload relays, you can extend the life of your electric motor and prevent damage that might cost you a considerable amount of money for maintenance or replacement of the motor.
In addition , the thermal overload relay function also helps to improve the efficiency and performance of the electric motor, and protects the electric motor from overuse conditions and rough environments.
By understanding the definition of Thermal overload relay correctly, you will more easily understand how this component can protect your electric motor from damage due to overheating or overload.
When Does Thermal Overload Relay Work?
Thermal overload relay (TOR) works when there is overheating or overload on the electric motor. There are several factors that can cause TOR to work, including:
- Environmental temperature: If the ambient temperature around the electric motor is too high, then this may trigger the TOR to work.
- Electric current: If the electric current that is being flowed through the electric motor is too large, TOR will serve to protect the motor from damage due to overheating.
- Motor component damage: If there is damage to the electric motor component, then this can cause overheating and trigger TOR performance.
In maintaining an electric motor, it is important to understand the things that can cause TOR to work in order to avoid damage and optimize the performance of your electric motor.
Parts of Thermal Overload Relay Parts
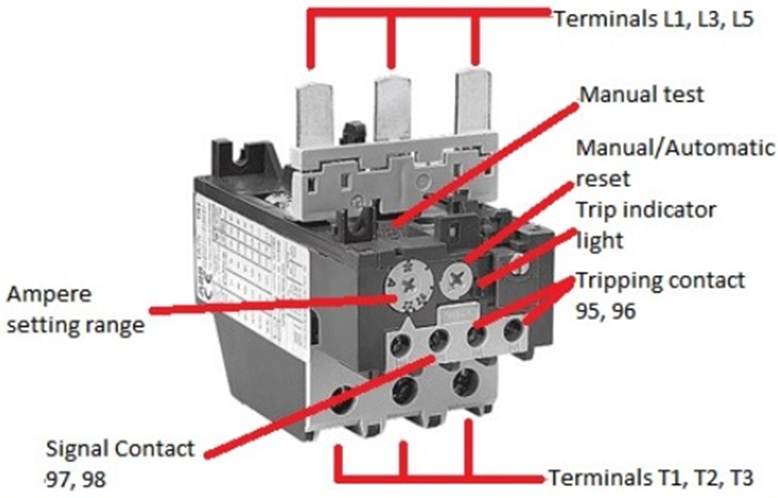
TOR component image example
Thermal Overload Relay (TOR) consists of several main components that play an important role in protecting the electric motor from overheating or overload. Here are 8 components of TOR that you should know:
| TOR components | Function |
| Heater Element | Detects the magnitude of the current and heats up to trigger the switch contact discharge |
| Current Coil | Measuring the current flowing through an electric motor for thermal readings |
| Bi-Metal Strip | Is a combination of two metals used in thermal switches to disconnect electrical power |
| Contact Terminal | Acts as a gateway between the TOR electrical breaker and the contactor |
| Contact Spring | Responsible for opening and closing the switch when there is a rise in temperature |
| Reset Mechanism | Serves to restore the position of the switch contacts to their original position after being triggered by overload or overheating |
| Test Button | Used to perform diagnostic tests on TOR components |
| Trip Indicator | Flags or indicators when switch contacts have been triggered |
Understanding the functions and roles of each TOR component is critical to TOR maintenance and troubleshooting. In the following article, we will discuss the TOR function in more detail.
Thermal Overload Relay Symbol
Thermal Overload Relay Symbol Image
The TOR symbol is a graphical representation of the component. In electrical diagrams, the symbol TOR is often used to indicate where this component is placed. This symbol also simplifies the interpretation of electrical diagrams to facilitate understanding of the functions of an electrical system.
The TOR symbol has three basic elements: a quadrilateral image, an arrow symbol, and a letter indicating its function. The quadrilateral image represents the thermal overload relay, while the arrow symbol indicates the direction of the electric current passing through the component.
The letters indicating its function are located inside the quadrilateral image. The most commonly used letters are “NO” or “NC”. “NO” stands for Normally Open, meaning that the contact is open under normal conditions and will close when TOR is working. “NC” stands for Normally Closed, meaning that the contact is closed under normal conditions and will open when TOR is working.
TOR function
Thermal Overload Relay (TOR) has the main function of protecting your electric motor from overheating and overload. TOR is able to detect excessive temperatures in electric motors and take measures to prevent further damage.
This component is very important in maintaining the performance of the electric motor at an optimal level. The function of TOR in maintaining the condition of the electric motor is very important, especially in long-term use and when used in harsh environments.
In particular, the function of TOR is to regulate the electric current entering the electric motor by cutting off the flow of electricity when the temperature of the electric motor reaches an unsafe temperature.
This is done in order to prevent damage to the electric motor and save its internal components. Without TOR, the electric motor can overheat and suffer irreparable damage, and must be replaced with a new one.
Working Principle of TOR
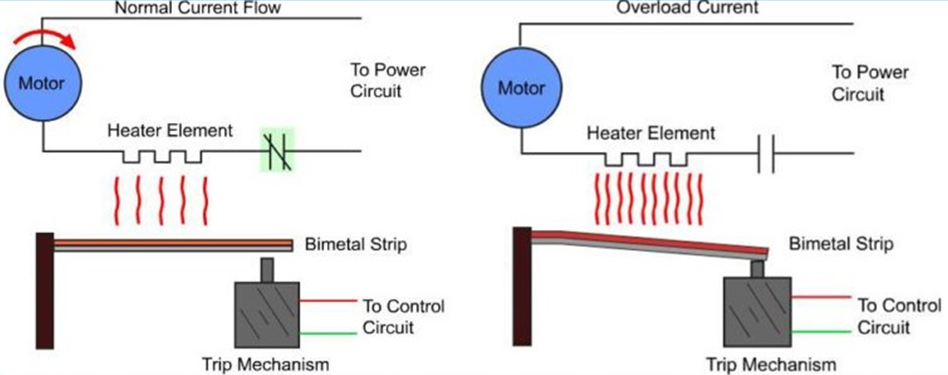
The way Thermal Overload Relay / TOR works is based on detecting excess temperature in electric motors. When the temperature rises above the predetermined limit, TOR will take measures to protect your electric motor from further damage.
This overtemperature detection process begins with temperature measurement by sensors in TOR. If the temperature is detected above the preset limit, there will be an output signal from TOR that will cut off the electrical power. This will stop the electric motor so that the temperature can return to normal before the motor is restarted.
The working principle of Thermal Overload Relay is very important in maintaining the performance and service life of your electric motor. By using TOR correctly, you can prevent damage from overheating or overload, thus saving on maintenance and repair costs of electric motors.
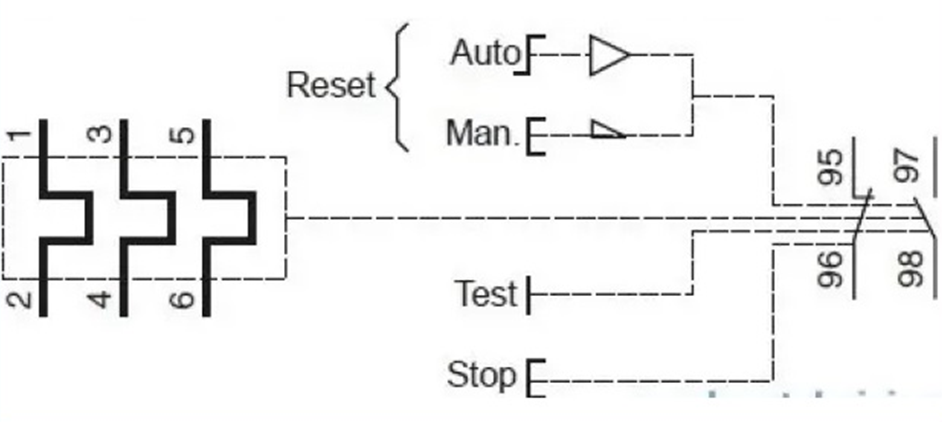
The working mechanism of the Thermal Overload Relay itself is very simple and very easy to understand. When the electric current through the resistance wire is above the normal limit, the bimetal will trip. That is, the bottom of the bimetal will curve to the left, pushing the slide in the same direction.
With this friction, the contact arm at the bottom will be pushed to the left, releasing the NC (Normally Close) 95-96 contacts, and connecting the NO (Normally Open) 97-98 contacts. Thus, excessive electric current will not reach the electronic devices in the circuit.
Now we will discuss the working principle of Thermal Overload Relay in regulating its operation. There are two TOR operation setting options, namely manual mode and automatic mode. Here’s the review:
Thermal Overload Relay Mode Manual
Manual mode allows you to manually set the operation of TOR. Here is how to set the Thermal Overload Relay in manual mode:
- Through the control panel, find the temperature setting.
- Specify the value of the electric current you want to set.
- Determine the desired time value before the Thermal Overload Relay disconnects electrical power.
- Customize to your needs.
- Test the setting by running an electric motor.
Make sure the settings you make are in accordance with the needs of your electric motor in order to protect the electric motor from damage.
Automatic Thermal Overload Relay Mode
Automatic mode allows the Thermal Overload Relay to operate automatically according to the temperature of the electric motor. Here is how to set TOR in automatic mode:
- Turn on the electric motor.
- After the electric motor reaches normal temperature, the operation of TOR will switch to automatic mode.
- SWitch Thermal Overload Relay to automatic mode.
- Make sure the temperature setting matches the needs of your electric motor.
- Run the electric motor to make sure the TOR works automatically.
Now you know how to set up TOR in manual and automatic mode. Make sure you know your electric motor needs before setting up TOR appropriately.
Conclusion
From all the explanations that have been discussed, it can be concluded that the thermal overload relay (TOR) is a very important component in protecting electric motors from damage due to overheating or overload.
TOR serves as a temperature detector on the electric motor, and when the temperature exceeds the specified limit, TOR will cut off the electrical power to the electric motor, thus minimizing damage. TOR consists of several components such as coils, NO contacts, NC, bimetallic, etc.
To set TOR, there are two modes, namely manual and automatic mode. Manual mode makes it easy for users to set TOR operation manually, while automatic mode allows TOR to operate automatically according to the temperature of the electric motor.
In optimizing the use of TOR, it is necessary to pay attention to several factors that can trigger TOR to work such as excessive ambient temperature and current. By understanding the effective use of TOR, the service life of electric motors can be increased and reduce the risk of costly damage.
This is a complete explanation of the thermal overload relay (TOR) and everything you need to know about this component in protecting the electric motor from damage. Hopefully the information provided can be useful for electric motorcycle users.
Read also Definition of Static Electricity and Examples
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is a thermal overload relay (TOR)?
A thermal overload relay (TOR) is a component used to protect an electric motor from overheating.
-
What is the commonly used TOR symbol in electrical diagrams?
A commonly used thermal overload relay symbol is a drawing of three circles connected by a straight line.
-
What are the components of TOR?
The components of thermal overload relay consist of bimetallic contacts, heater elements, coils, contacters, bimetal strips, reset buttons, test buttons, and connection cables.
-
What are the main functions of TOR?
The main function of thermal overload relays is to detect excessive temperatures in electric motors and take measures to prevent further damage.
-
How does TOR work?
Thermal overload relays work by detecting excess temperatures in electric motors and disconnecting electrical power automatically or manually.
-
How to set TOR in manual and automatic mode?
To adjust the thermal overload relay in manual mode, you need to move the reset button lever and test button manually. To set up thermal overload relay in automatic mode, you need to follow the step-by-step guide provided.
-
What are the factors that can cause TOR to work?
Factors that can cause thermal overload relays to work include high ambient temperatures, excessive current, or abnormal motor performance.
Thus a complete explanation of the wikielektronika.com version of the Thermal Overload Relay. In closing, we also tell you that there are several other things to consider in the maintenance of an electric motor.
Using a Thermal Overload Relay alone is not enough to guarantee optimal electric motor performance. Here is some additional information that will help you in maintaining your electric motor effectively:
- Make sure your electric motor is properly installed. Before operating the electric motor, make sure that it is properly installed on the mechanical system. Also make sure that the motor is connected to a stable power source and complies with the specified specifications.
- Carry out regular maintenance. Electric motors need to be maintained periodically to ensure their performance remains optimal. Perform regular cleaning and lubrication of motor components. Replace worn or damaged components immediately to prevent further damage.
- Use additional electrical safeguards if needed. In addition to TOR, there are many additional types of electrical safeguards that can help protect your electric motor from damage from various electrical problems such as surges and current interruptions. Consider installing additional electrical safeguards if needed.
By paying attention to the above factors, you can ensure that your electric motor is working properly and durable.