Thermocouple and its Working Principles – Thermocouple is a type of temperature sensor used to detect or measure temperature through two different types of metal conductors combined at the end, causing a “Thermo-electric” effect. The thermo-electric effect on thermocouples was discovered by an Estonian physicist named Thomas Johann Seebeck in 1821, where a metal conductor that is given a gradient heat difference will produce an electrical voltage. The difference in electrical voltage between these two junctions is called the “Seeback” Effect.
Thermocouples are one of the most popular types of temperature sensors and are often used in various electrical and electronic equipment related to Temperature. Some of the advantages of thermocouples that make it popular are its rapid response to temperature changes and also its wide operational temperature range, which ranges from -200 °C to 2000 °C. In addition to its fast response and wide temperature range, thermocouples are also resistant to shocks/vibrations and easy to use.
Thermocouple Working Principles
The working principle of Thermocouple is quite easy and simple. Basically thermocouples consist of only two metal wire conductors of different types and combined ends. One type of metal conductor contained in thermocouples will serve as a reference with a constant (fixed) temperature while the other as a conductor metal that detects hot temperatures.
For more details on the Principles of Thermocouple Work, let’s take a look at the image below:
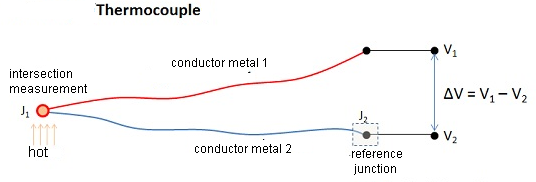
Based on the figure above, when both junctions or junctions have the same temperature, the difference in potential or electrical voltage through the two intersections is “ZERO” or V1 = V2. However, when the junction connected in the circuit is given a hot temperature or connected to the measuring object, there will be a temperature difference between the two intersections which then produces an electric voltage whose value is proportional to the heat it receives or V1 – V2. The electrical voltage caused by this is generally around 1 μV – 70μV at each degree Celsius. The voltage is then converted according to the established reference table so as to produce measurements that can be understood by us.
Read Also Definition of Transducer and its types
Types of Thermocouple
Thermocouples are available in a wide variety of temperature ranges and types of materials. Basically, the combination of different types of conductor metals will produce different operational temperature ranges. The following are the types or types of thermocouples that are commonly used based on International Standards.
Thermocouple Type E
Positive Conductor Metal Material : Nickel-ChromiumThe Negative Conductor Metal System : Constantabout Temperature : -200 °C – 900 °C
Type J thermocouple
Positive Conductor Metal Material : Iron (Iron)Negative Conductor Metal Material : Constantabout Temperature : 0°C – 750°C
Type K thermocouple
Positive Conductor Metal Material : Nickel-ChromiumThe Negative Conductor Metal System : Nickel-AluminumAbout Temperature : -200 °C – 1250 °C
Type N thermocouple
Positive Conductor Metal Material : NicrosilThe Negative Conductor Metal Change : NisilAbout Temperature : 0 °C – 1250 °C
Type T thermocouple
Positive Conductor Metal Material : Copper (Copper)Negative Conductor Metal Material : Constantabout Temperature : -200°C – 350°C
Type U thermocouple (Type S and Type R compensation)
Positive Conductor Metal Material : Copper (Copper)Negative Conductor Metal Material : Copper-NickelAbout Temperature : 0°C – 1450°C




